
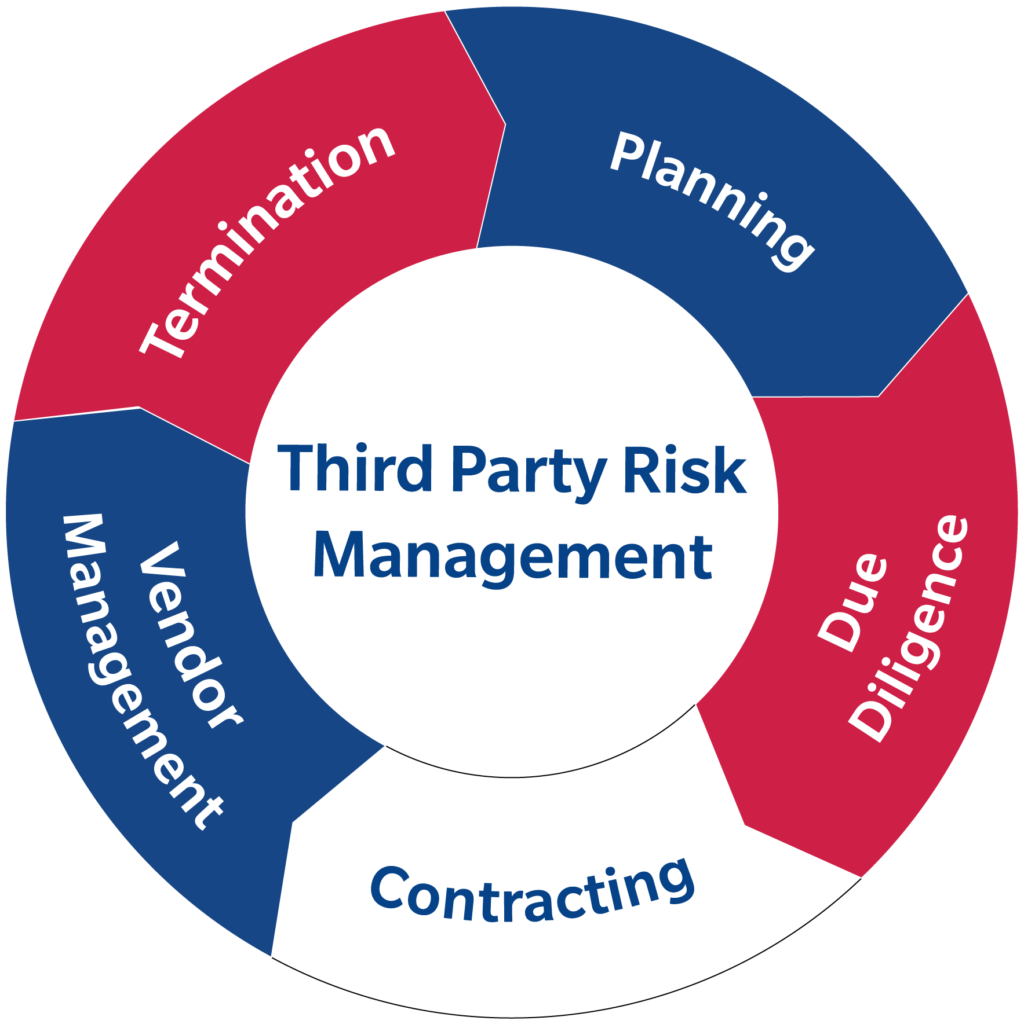
Planning – The first determination to make is whether a third party is necessary.The outline below follows this trend but broken down into three broad phases with sub-steps, for a more comprehensive explanation. Most of the published lifecycles use a five to eight-step process. The OCC provides an outline targeting financial institutions, while other security experts provide a slightly broader lifecycle addressing global standards.

Lifecycles are rarely identical because each entity has a different perspective, and it’s no different from a third-party risk management lifecycle. The benefits of third parties are numerable including lower costs, access to scarce knowledge, and improved strategic agility, but with the benefits comes a responsibility to implement proper oversight. As globalization continues, the third-party network becomes more complex. An extended enterprise encompasses anything from an alliance to a joint venture to a subsidiary. Today, a business’s environment includes an “extended enterprise.” Suppliers, support service providers, sales agents/distributors, and affiliated organizations. If a third party fails to comply with industry standards, engages in any unethical business practices, or experiences a security breach, the hiring firm will likely be impacted and even receive the majority of the blame for lack of third-party oversight. The generally accepted position is that you know who they are, you have vetted them and you are in control of the activities for which you hired them.

Companies that hire third parties assume responsibility for their actions and any mistakes or infractions that occur. A third party partnership requires oversight and communication as long as the relationship exists. Vetting a third party prior to signing a contract is not enough on its own. Learn about the third-party risk management process and lifecycle here.
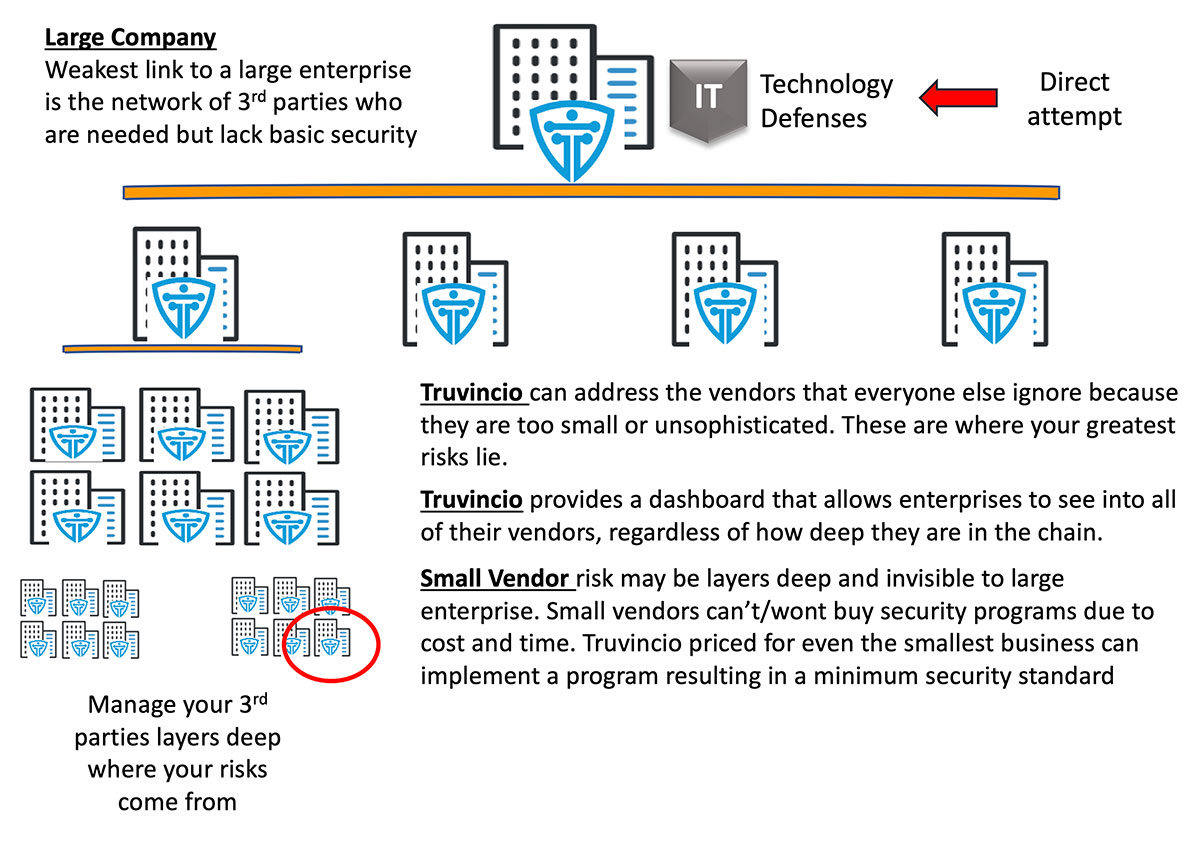
However, establishing a third-party partnership doesn’t happen overnight. In relation to cybersecurity, third parties have become especially helpful for conducting security assessments, monitoring networks, expanding services offered. But with outside assistance comes more risk. Companies rarely control every aspect of their supply chains and now use third parties to fill knowledge, time, or money gaps. The times of vertical management no longer serve as the best option for efficiency and cost-effectiveness.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
